Although a CNC machine may appear to be a complicated piece of machinery, dissecting it into its component parts makes it much easier to understand. These devices have revolutionized manufacturing by using a computer to control tools used to create parts.
Understanding the components is a great first step, regardless of your interest in CNC milling, CNC turned components, or just your desire to learn more. This information is essential for a business like Global Precision Pvt Ltd, which collaborates with CNC components manufacturers.
How to Do CNC Machines Parts Work?
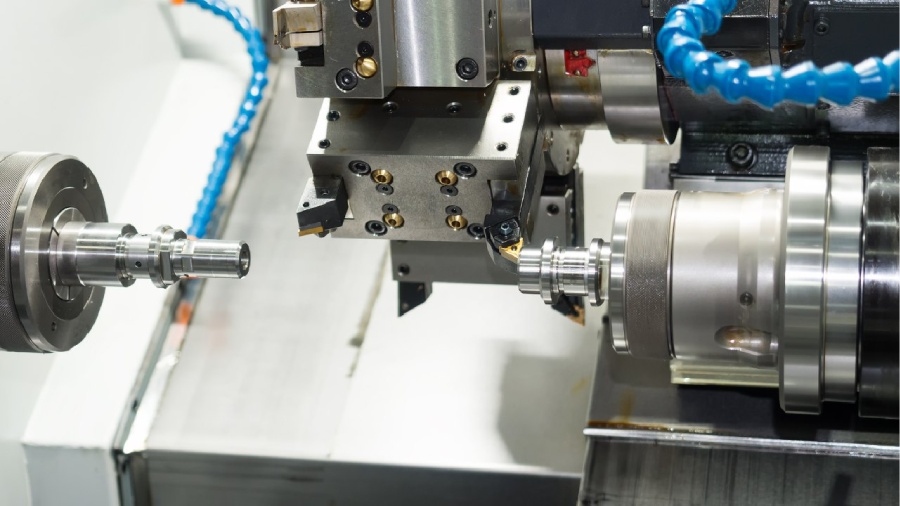

A combination of mechanical precision and computer programming powers CNC machines. The procedure starts with a set of digital instructions called G-code, which acts as the operation’s blueprint. Everything the machine does is controlled by this code, including the spindle’s speed and the cutting tool’s path. The machine then turns a raw piece of material into a finished part by carrying out these commands with amazing accuracy.
The main benefit of CNC machining is its capacity to provide accuracy and precision that are just not possible with manual techniques. Parts with incredibly tight tolerances and complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to create otherwise can be produced by CNC machines.
In sectors like automotive manufacturing, medical devices, and aerospace, this degree of accuracy is essential. Additionally, the high degree of repeatability provided by CNC machines guarantees that each part produced is an exact replica of the previous one, which is essential for mass production and quality control.
G-code is the foundation of any CNC operation. However, where is the source of this code? Not every part is handwritten. Rather, engineers and designers employ specialized software known as Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM).
The G-code required to create the desired part is automatically generated by CAM software using a 3D model of the part. Tool paths, cutting speeds, and other crucial parameters are defined during this process. This automation removes the chance of human error in programming and saves a ton of time.
List Of Major Parts Of CNC Machine:
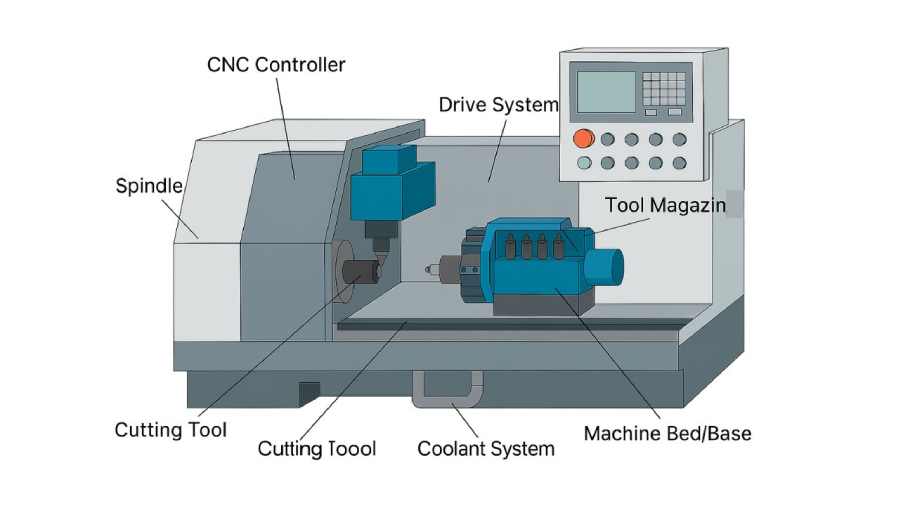
The following is a basic explanation of the main components of a CNC machine –
1. CNC Controller – Consider the CNC controller to be the machine’s “brain.” A computer known as the CNC Controller reads instructions from a program known as G-code. After that, it converts those commands into exact motions for the machine’s motors. It regulates every aspect, including the cutting tool’s path and spindle speed. The machine would just be a collection of metal parts without this part. It serves as the focal point of all activities.
2. Spindle – The cutting tool is held in place by a revolving shaft called the spindle. It has a motor that gives it the ability to spin at extremely high speeds. The purpose of the spindle is to supply the force and speed required for material cutting, drilling, or shaping. A rotating end mill is held in place by the spindle of machines that produce CNC milling components. The spindle of a lathe used to create CNC-turned parts holds the workpiece in place while spinning it in opposition to a stationary tool. The performance of a machine is largely dependent on the spindle’s power and speed.
3. Drive System – The motors and gears that move the machine’s axes are part of the drive system. To move the cutting tool or the workpiece along the X, Y, and Z axes, these motors are precisely controlled by the CNC controller. The drive system’s speed and accuracy are essential for producing precise, high-quality parts. Because even the smallest mistake in the drive system can result in a defective part, CNC components manufacturers make investments in top-notch drive systems.
4. Cutting Tool – The component that actually cuts the material is called the cutting tool. The job determines the kind of cutting tool to use. It might be a turning tool for a lathe, a drill bit for drilling, or an end mill for milling. To withstand the forces and heat of cutting, these tools are frequently constructed from extremely hard materials like high-speed steel or carbide. They are available in a variety of sizes and shapes to add various features to a part.
5. Machine Bed/Base – This serves as the machine’s base. Usually constructed of steel or cast iron, the machine bed is a substantial, sturdy base. In order to absorb vibrations during the cutting process, its weight and stiffness are crucial. This stability contributes to the final part’s accuracy and smooth surface. During operation, it is the anchor that maintains stability.
6. Tool Magazine/Changer – A tool magazine is a feature of many contemporary CNC machines, particularly those utilized by producers of CNC components such as Global Precision Pvt Ltd. A variety of cutting tools are kept in this storage carousel. A robotic arm that rapidly replaces the tools in the spindle is the automatic tool changer. This increases efficiency and saves a great deal of time by enabling the machine to carry out several tasks, such as drilling, milling, and tapping, without a human having to change the tools by hand.
7. Coolant System – Cutting metal produces a lot of heat, which can harm the workpiece and the tool. To cool the cutting area, lubricate the cut, and remove chips, the coolant system sprays a liquid onto it. By keeping the material from warping, this not only prolongs the cutting tool’s life but also enhances the quality of the final product.
The remarkable accuracy and productivity we observe in contemporary manufacturing are made possible by the cooperation of these seven elements.

